With the growing prominence of cloud computing, there’s a pressing demand for seamless, cost-effective deployment of large language models (LLMs), AI, and batch jobs across various cloud platforms. Enter SkyPilot, designed to tackle this challenge. It not only streamlines cloud infrastructure operations, allowing users to deploy and scale jobs effortlessly across any cloud platform, but also intelligently compares real-time GPU prices from multiple providers. This ensures users select the most cost-effective platform for their tasks, leading to substantial cost savings and optimized GPU availability. Consequently, SkyPilot responds to the market’s call for efficient and affordable cloud resource utilization. By leveraging SkyPilot, both enterprises and individual developers can harness the full potential of GPUs, thereby advancing artificial intelligence and big data technologies and ushering in new horizons for the cloud computing industry.
SkyPilot
SkyPilot is a framework designed for large language models (LLMs), AI, and batch jobs that can run on any cloud platform. It’s a CLI tool and is very convenient for users familiar with the command line. With just one command, a complete cloud environment can be initiated without delving into the specifics of VMs, networks, or security group configurations. Compared with Terraform, SkyPilot offers faster speed and a better experience. Most importantly, it allows users to use the same configuration on multiple cloud platforms, saving a lot of learning and adaptation time.
Key advantages of SkyPilot include:
- Cloud Infrastructure Abstraction: Simplifies the process of launching jobs and clusters on any cloud, making it easy to scale and access object storage.
- Maximized GPU Availability: Automatically allocates resources in all accessible regions and clouds, achieving automatic failover.
- Reduced Cloud Costs: Uses spot VMs to save costs, automatically selects the cheapest resources, and shuts down idle clusters.
- No Code Changes Needed: Compatible with existing GPU, TPU, and CPU workloads without code modifications.
In addition to these advantages, a core feature of SkyPilot is simplifying cloud infrastructure management. Its key features include:
- Managed Spot: Optimizes resource allocation by leveraging spot VMs (temporary virtual machines), offering users a 3-6x cost saving. It also ensures stable job operation in case of preemption events.
- Smarter Optimizer: Smartly chooses the cheapest virtual machine, region, or cloud platform to further save user costs.
- Other Features and Characteristics:
- Cross-Cloud Platform Support: Runs on AWS, Azure, GCP, and other cloud platforms.
- Easy Expansion: Easily runs multiple jobs, which are automatically managed to ensure effective resource utilization.
- Object Storage Access: Simplifies access to object storage like S3, GCS, R2, etc., facilitating data management and storage.
Currently supported cloud providers include AWS, Azure, GCP, Lambda Cloud, IBM, Samsung, OCI, Cloudflare, and Kubernetes:

Quick Start
Here’s how to use SkyPilot to deploy the Llama-2 Chatbot on Azure.
Installation
First, ensure you have Python 3.7 or higher installed on your system. For Apple Silicon, it’s recommended to use Python 3.8 or higher. Here’s how to install SkyPilot:
Create and activate a new conda environment (recommended but not mandatory):
conda create -y -n sky python=3.8 conda activate skyInstall SkyPilot using pip. Depending on the cloud service providers you plan to use with SkyPilot, you can choose additional installation options. For instance, if you wish to use SkyPilot on AWS and Azure, run:
pip install "skypilot[aws,azure]"
Alternatively, you can install all available additional options:
pip install "skypilot[all]"
Moreover, you can opt to install the latest nightly build:
pip install -U "skypilot-nightly[all]"
Or install SkyPilot from source:
git clone https://github.com/skypilot-org/skypilot.git
cd skypilot
pip install ".[all]"
Configuration
After installation, some initial configurations are necessary to connect to your cloud provider. These configuration steps may vary depending on the cloud provider. The overall configuration process is relatively simple. If you’ve already set up the corresponding cloud CLI locally, you can use the following command to check if SkyPilot can access it properly:
sky check
You’ll see output indicating the access status for each cloud:
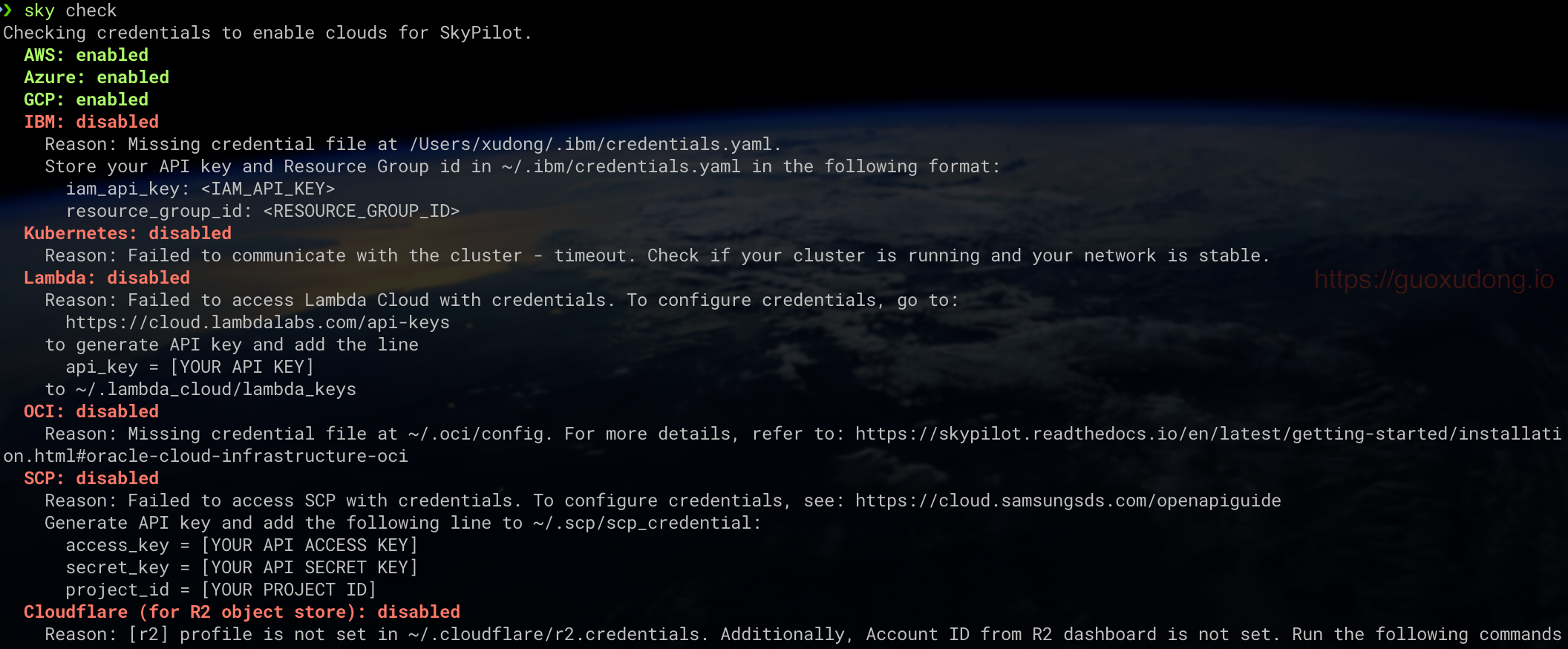
Next, we’ll briefly cover how to configure for Azure. For configurations for other clouds, refer to the official documentation.
- Download and install the Azure CLI.
- Log in to the Azure CLI with
az login. - Retrieve your account’s
subscription_idlist usingaz account subscription list. Set your desired subscription with
az account set -s <subscription_id>.# Login az login # Set the subscription to use az account set -s <subscription_id>Finally, run
sky checkagain to verify the successful configuration.
Creating and Running Llama-2 Chatbot
Outlined below are the preliminary steps. For a comprehensive guide, please consult the official documentation.
Pre-requisites
- Visit this page to apply for the access to the Llama-2 model.
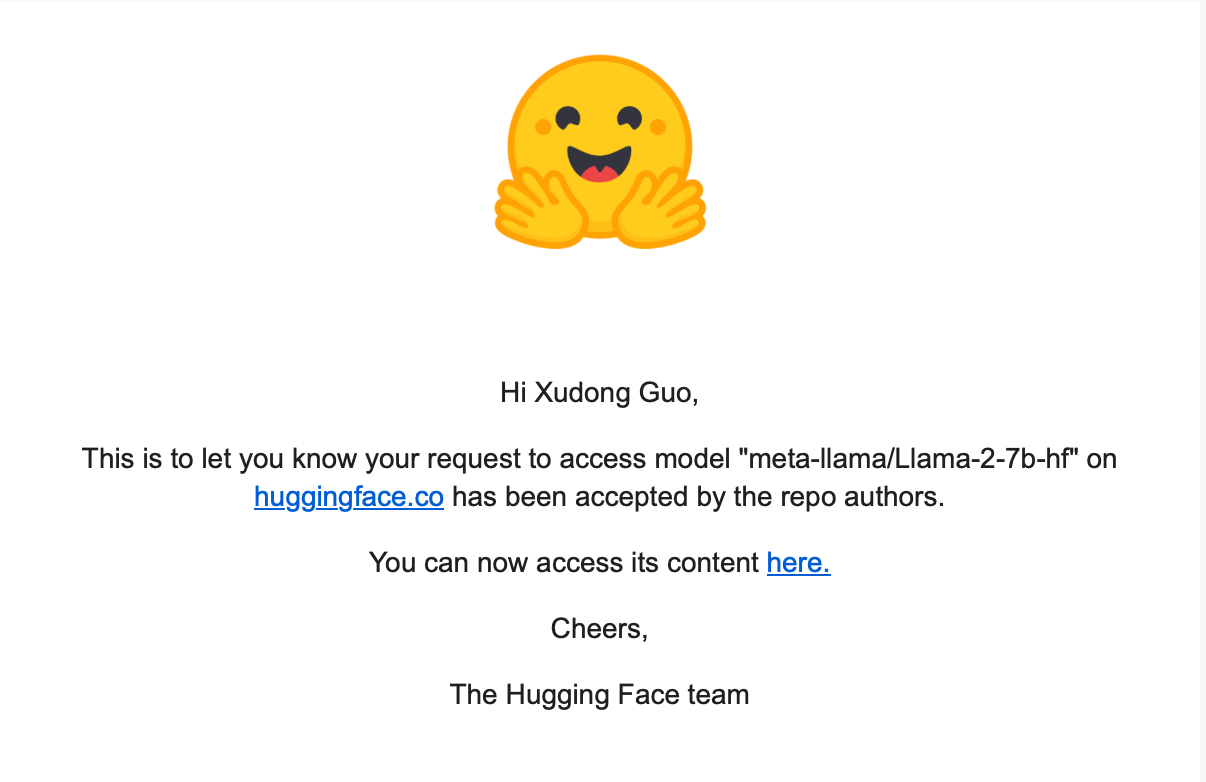
- Get the access token from huggingface, generate a read-only access token on huggingface, and ensure your huggingface account can access the Llama-2 model.
Fill the access token in the
chatbot-meta.yamlfile.envs: MODEL_SIZE: 7 HF_TOKEN: <your-huggingface-token>
Running Llama-2 Chatbot with SkyPilot
Create a new YAML file named
chatbot-meta.yamland add the following content:resources: accelerators: V100:1 disk_size: 1024 envs: MODEL_SIZE: 7 HF_TOKEN: <your-huggingface-token> # TODO: Replace with huggingface token setup: | set -ex git clone https://github.com/facebookresearch/llama.git || true cd ./llama pip install -e . cd - git clone https://github.com/skypilot-org/sky-llama.git || true cd sky-llama pip install torch==1.12.1+cu113 --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu113 pip install -r requirements.txt pip install -e . cd - # Download the model weights from the huggingface hub, as the official # download script has some issues. git config --global credential.helper cache sudo apt -y install git-lfs pip install transformers python -c "import huggingface_hub; huggingface_hub.login('${HF_TOKEN}', add_to_git_credential=True)" git clone https://huggingface.co/meta-llama/Llama-2-${MODEL_SIZE}b-chat wget https://github.com/tsl0922/ttyd/releases/download/1.7.2/ttyd.x86_64 sudo mv ttyd.x86_64 /usr/local/bin/ttyd sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/ttyd run: | cd sky-llama ttyd /bin/bash -c "torchrun --nproc_per_node $SKYPILOT_NUM_GPUS_PER_NODE chat.py --ckpt_dir ~/sky_workdir/Llama-2-${MODEL_SIZE}b-chat --tokenizer_path ~/sky_workdir/Llama-2-${MODEL_SIZE}b-chat/tokenizer.model"Run the following command to start the cluster and execute the task:
sky launch -c llama chatbot-meta.yaml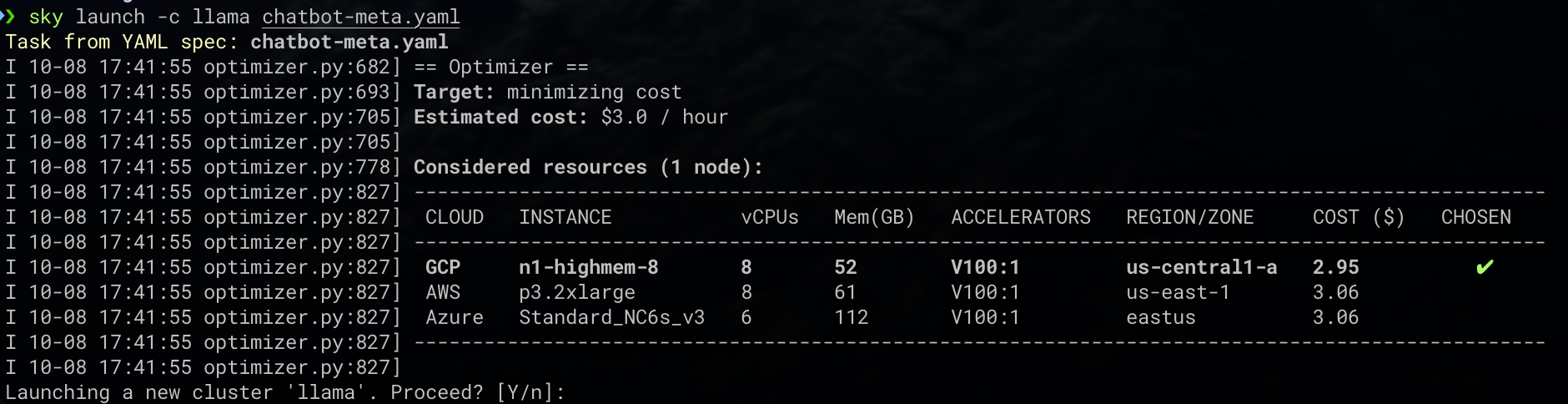
In the above steps,
llamais the name of the cluster, andchatbot-meta.yamlis the task configuration file. Within a few minutes, SkyPilot will complete cluster creation, configuration, and task execution on Azure’s V100 GPU.Open a new terminal and execute the following command to bind local
port 7681 to the cluster’s 7681 port:
```bash
ssh -L 7681:localhost:7681 llama
```
Open
http://localhost:7681in your browser and start chatting!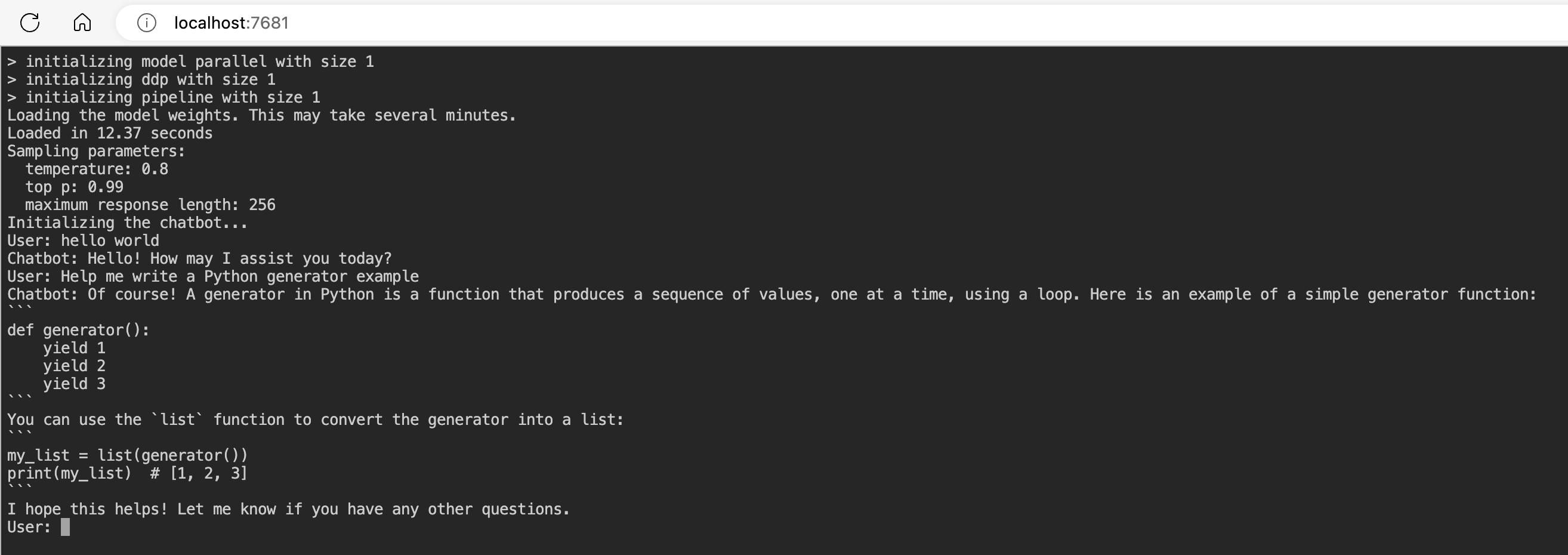
Cleaning Up
When you are done, you can use the following commands to stop or tear down the cluster:
Stop the cluster, run:
sky stop lama # or pass your custom name if you used "-c <other name>"Restart a stopped cluster and relaunch the Chatbot:
sky launch chatbot-meta.yaml -c llama --no-setupUsing
--no-setupaims to skip the setup step since the stopped cluster has retained its disk contents.To tear down the cluster (non-restartable), run:
sky down llama # or pass your custom name if you used "-c <other name>"
To see your clusters, run sky status, which is a single pane of glass for all your clusters across regions/clouds.
Advanced Usage
Beyond the basic methods mentioned above, SkyPilot has numerous advanced features. Here’s a brief introduction to some of them.
Show Supported GPU/TPU/Accelerators and Their Prices
The names and counts shown can be set in the accelerators field in task YAMLs, or in the --gpus flag in CLI commands. For example, if this table shows 8x V100s are supported, then the string V100:8 will be accepted by the above.
Different clouds have confusing GPU model names and their prices. SkyPilot has standardized the naming and pricing of the same GPU model and provides a show-gpus command to display currently supported GPU/TPU/accelerators and their prices:
sky show-gpus <gpu>
Public IP and Ports
If you prefer to access your clusters using ssh, you can use the following command to get the cluster’s Public IP:
sky status --ip <your-custom-name>
Moreover, if you wish to open some ports, you can use resources.ports to specify ports to open:
resources:
# ports: 8888
ports:
- 8888
- 10020-10040
- 20000-20010
SkyPilot also support opening ports through the CLI:
sky launch -c jupyter --ports 8888 jupyter_lab.yaml
Interactive Nodes
SkyPilot also offers interactive nodes, allowing users to quickly start specified single node VMs on clouds with simple CLI commands, without needing a YAML configuration file.
sky gpunodesky cpunodesky tpunode# Launch a default gpunode. sky gpunode # Do work, then log out. The node is kept running. Attach back to the # same node and do more work. sky gpunode # Create many interactive nodes by assigning names via --cluster (-c). sky gpunode -c node0 sky gpunode -c node1 # Port forward. sky gpunode --port-forward 8080 --port-forward 4650 -c cluster_name sky gpunode -p 8080 -p 4650 -c cluster_name # Sync current working directory to ~/workdir on the node. rsync -r . cluster_name:~/workdir
Show Estimated Cost of Launched Clusters
SkyPilot also provides a command to display the estimated cost of running clusters:
sky cost-report
Note: This CLI is experimental. The estimated cost is calculated based on the local cache of cluster status and may not be accurate.
Fetch Global Region Information for Azure and GCP
By default, SkyPilot supports most global regions on AWS, but only US regions on GCP and Azure. If you specify a region outside of the US, you might encounter an error like:
ValueError: Invalid region 'australiaeast'
List of supported azure regions: 'centralus, eastus, eastus2, northcentralus, southcentralus, westcentralus, westus, westus2, westus3'
If you wish to use all global regions, additional commands are required to fetch global region information for Azure and GCP:
version=$(python -c 'import sky; print(sky.clouds.service_catalog.constants.CATALOG_SCHEMA_VERSION)')
mkdir -p ~/.sky/catalogs/${version}
cd ~/.sky/catalogs/${version}
# GCP
pip install lxml
# Fetch all regions for GCP
python -m sky.clouds.service_catalog.data_fetchers.fetch_gcp --all-regions
# Azure
# Fetch all regions for Azure
python -m sky.clouds.service_catalog.data_fetchers.fetch_azure --all-regions
Conclusion
SkyPilot is a highly versatile and powerful tool that brings a new level of simplicity and efficiency to cloud infrastructure management, especially for large language models and AI batch jobs. By automatically selecting the cheapest and most effective resources, and providing a smooth user experience, SkyPilot is poised to be a game-changer for enterprises and developers in the cloud computing space. Whether you’re a solo developer or part of a large organization, SkyPilot offers features and benefits that can streamline your cloud operations, save costs, and ensure maximum efficiency. With an active and growing community, the future of SkyPilot looks very promising. Give it a try and experience the future of cloud computing today!